
CH 467 PIGEON SKELETON Dbios Charts
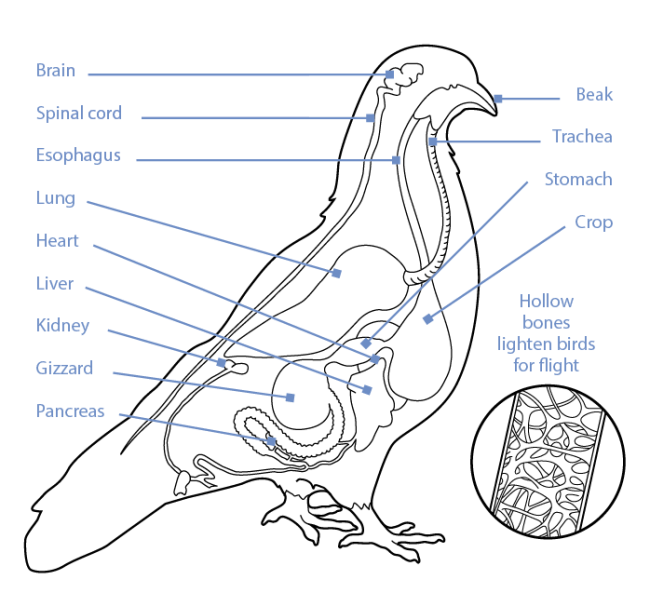
Bird anatomy, or the physiological structure of birds ' bodies, shows many unique adaptations, mostly aiding flight. Birds have a light skeletal system and light but powerful musculature which, along with circulatory and respiratory systems capable of very high metabolic rates and oxygen supply, permit the bird to fly.

Anatomie interne du pigeon illustration de vecteur. Illustration du interne 211917371
Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System In the respiratory system of a pigeon, there is a wide range of organs and tissues. These components of the bird anatomy allow it to breathe properly and ensure proper respiratory health.These organs include nostrils, air sacs, and many more.
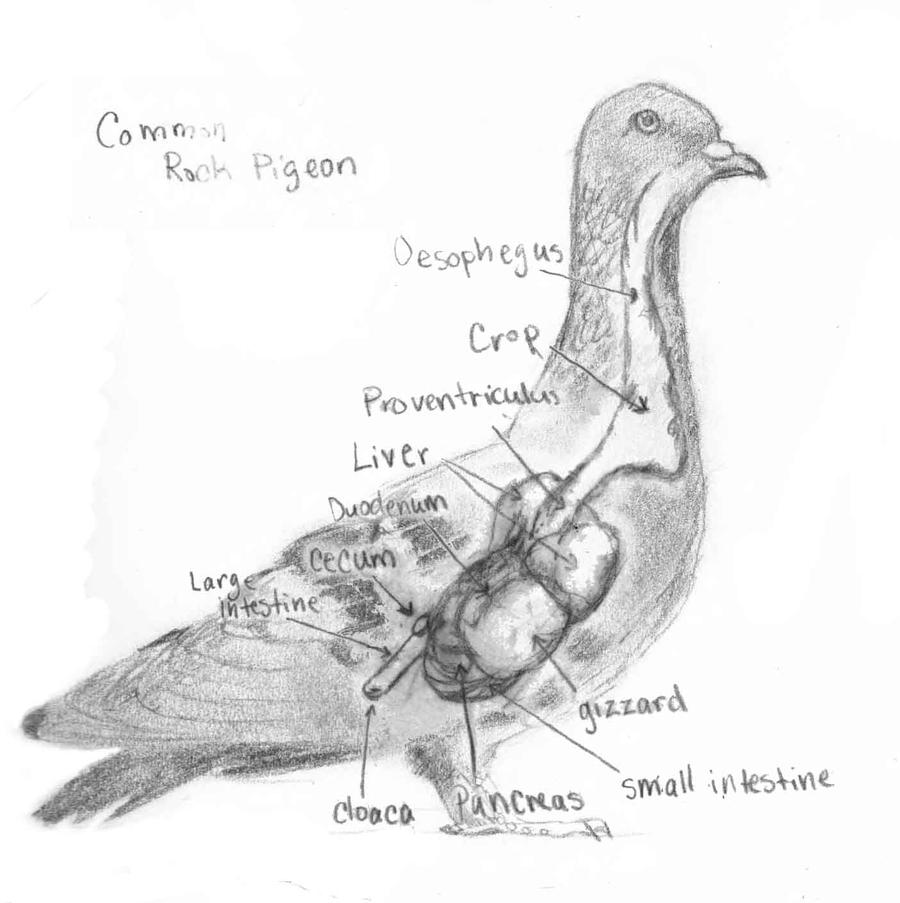
A Pigeon's Digestive System by Fishypaste on DeviantArt
Shape and Size: The spindle-shaped or fusiform body of Blue Rock Pigeon is about 33 cm in length and is well adapted for rapid movement through the air. Coloration: Except the eyes and the feet which are pink, rest of the body of pigeon is a salty gray with glistening metallic green and purple sheen on the upper breast and around the neck.
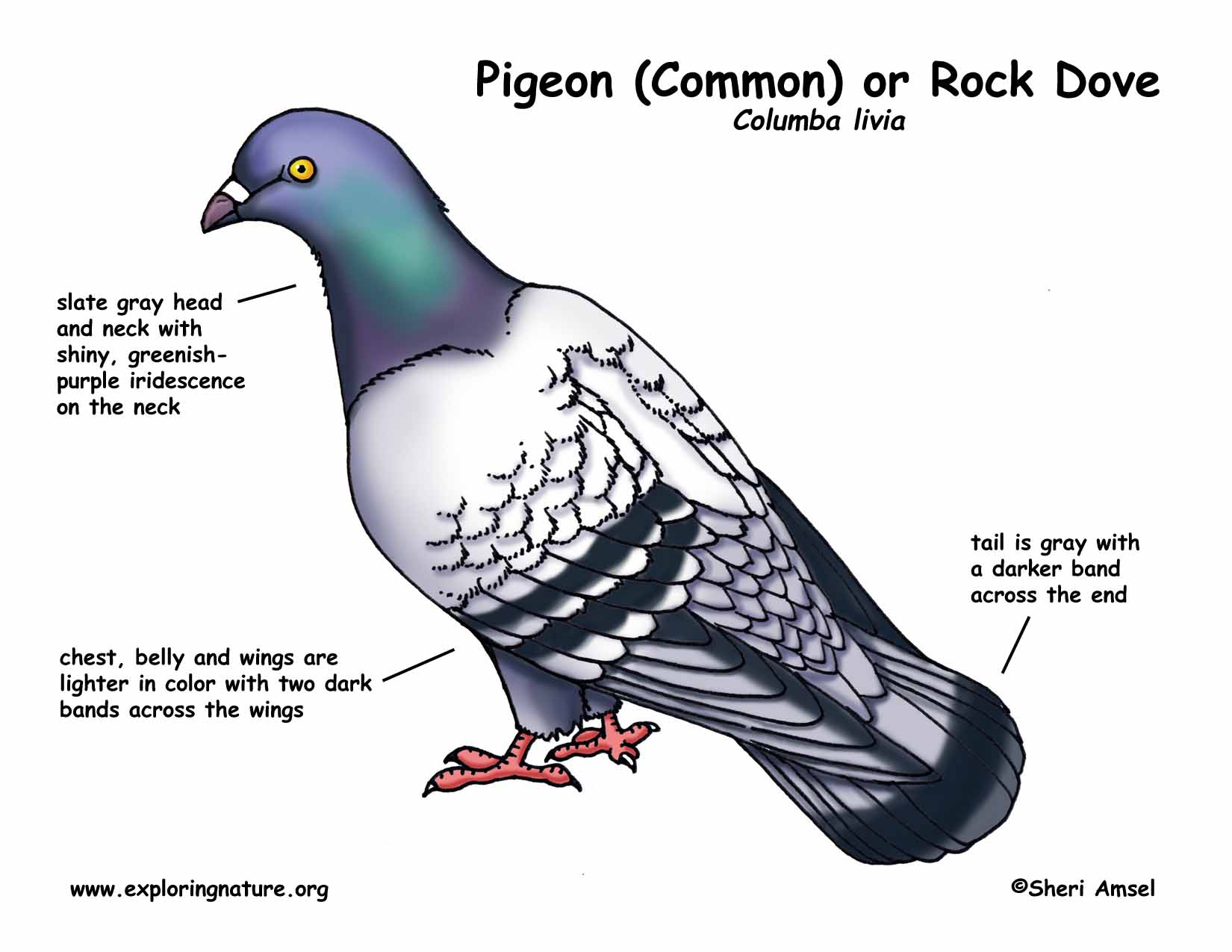
Pigeon or Rock Dove
1. Heart: The heart is four chambered 2 auricles and 2 ventricles. The sinus venosus is absent. External Structure: ADVERTISEMENTS: The heart of pigeon is large-sized, reddish in colour, triangular and compact. It lies midventrally in the thorax.
Reconsidering the Pigeon Discover Magazine
Projecting into the vitreous body from the blind spot, a characteristic structure, called pecten, is present (Fig. 9.32B). The pecten is highly variable in size and shape in different birds. In pigeon, it is composed of a thin dark pigmented plate. This plate is folded fanwise and assumes the form of a comb.

Pigeon skeleton Atlas of Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy
Posterior view of pigeon skeleton. CC-BY Alexandra Caffrey. Posterior view of pigeon forelimb and thoracic region. CC-BY Alexandra Caffrey. Lateral view of pigeon thoracic cage. CC-BY Alexandra Caffrey & Kristen Roosa.
The Complete Guide To Pigeons (Columbidae) Pigeonpedia
Pigeon Anatomy. High Resolution PDF for Printing. Click Here. Citing Research References. When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).

Anatomy of pigeon bird isolated on white background illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
The Cornell How much do you know about bird anatomy? Test yourself with an interactive reference guide to all the important anatomical systems in a bird.

Pigeon Anatomy Crop
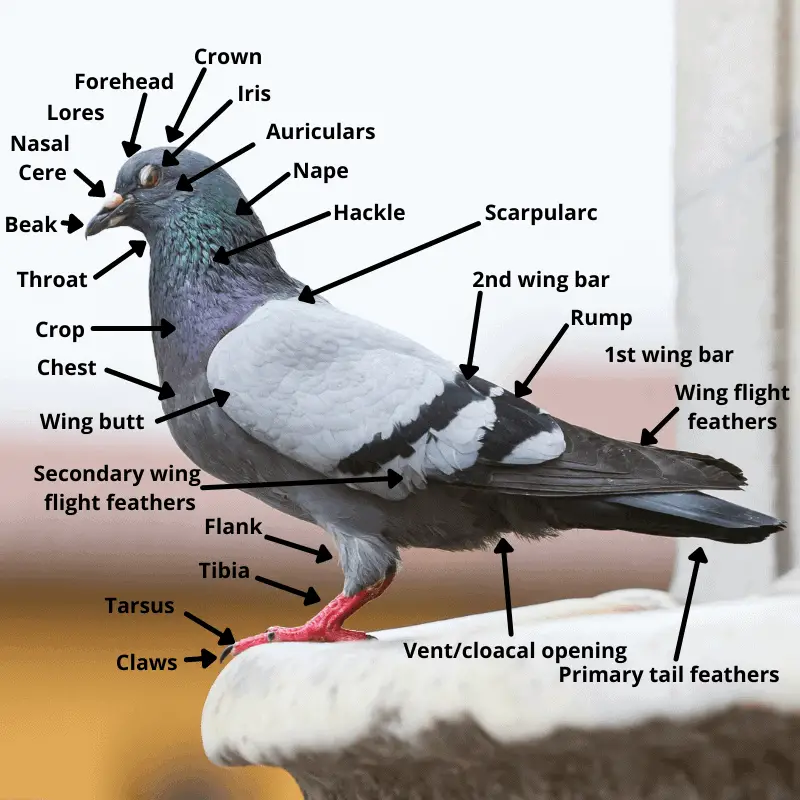
(i) Head: ADVERTISEMENTS: The head is small, round and anteriorly pointed. It contains the following structures: (a) Mouth: It is a wide gap at the anterior end of head and bounded by upper and lower beaks. Both the beaks are covered by a sheath called horny sheath or rhamphothecae.
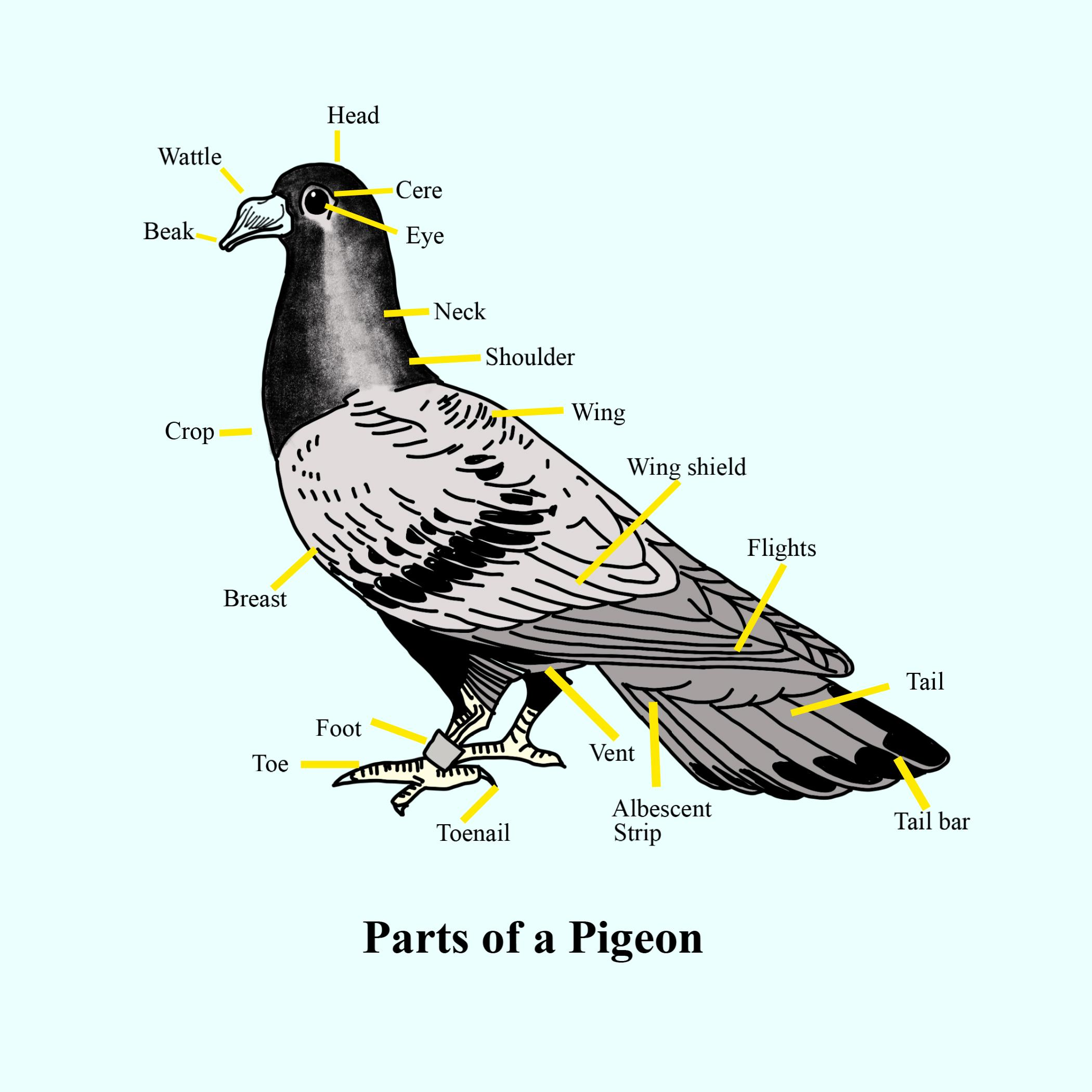
Anatomy Of A Pigeon lupon.gov.ph
Columbidae (/ k ə ˈ l ʌ m b ɪ d iː / kə-LUM-bih-dee) is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons.It is the only family in the order Columbiformes.These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres.They primarily feed on plants, and can be taxonomically divided amongst granivores, that feed mostly on the ground on seeds.
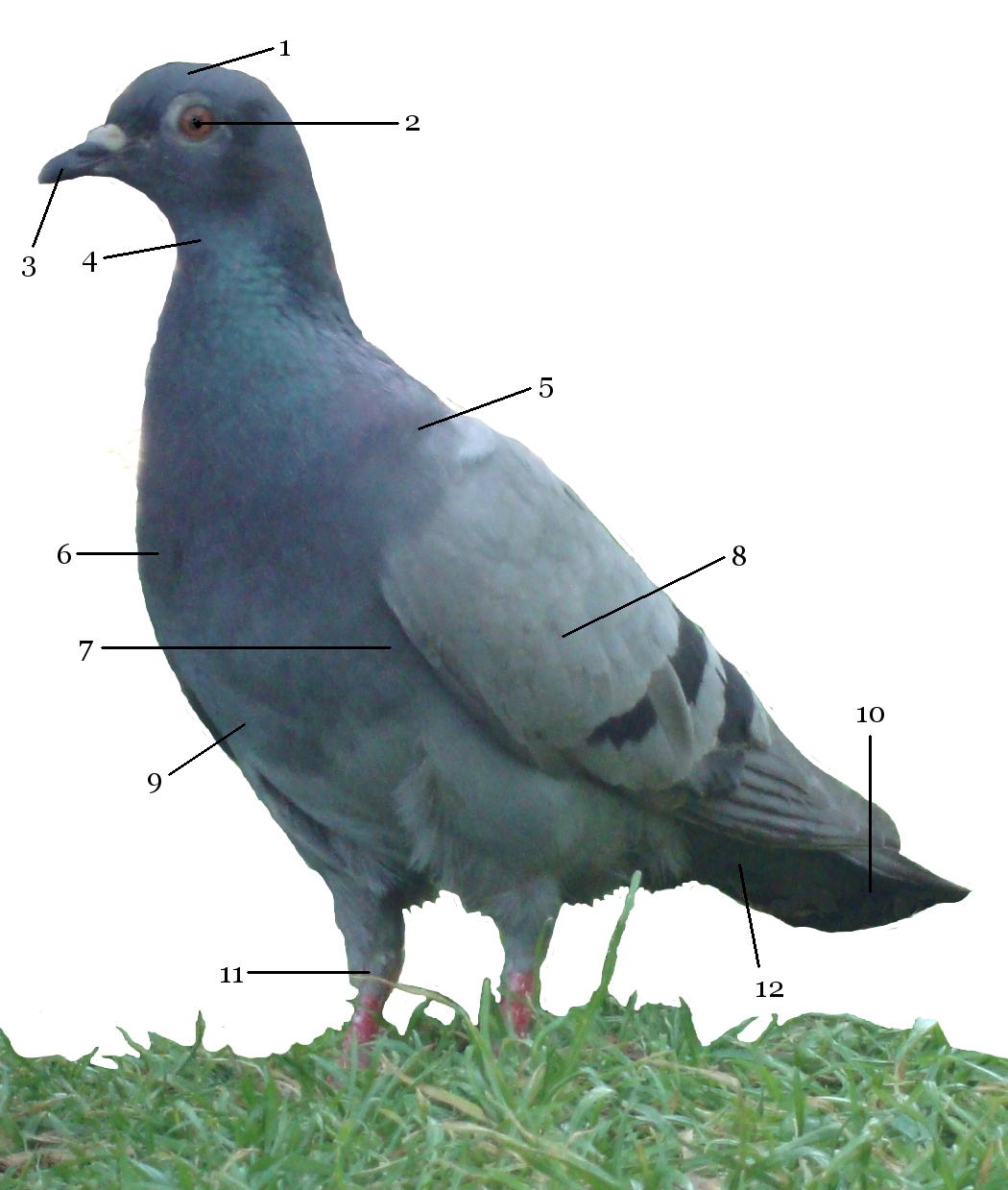
London pigeons
Although pigeons and doves are a diverse group of birds, they do share some clinically significant anatomy and physiology, including a large, bilobed crop or ingluvies, crop milk production, as well as a vascular plexus found in the subcutis of pigeons.

Pigeon Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The types are: 1. Muscular System 2. Digestive System 3. Respiratory System 4. Circulatory System 5. Lymphatic System 6. Nervous System 7. Endocrine System 8. Excretory System 9. Reproductive System. Type # 1. Muscular System: The muscular system of pigeon is extremely modified to meet the requirements of its peculiar way of life.
Anatomy Of A Pigeon lupon.gov.ph
The structure of the eye of the homing pigeon. Journal of Comparative Psychology, 1938, 25, 249-272. Google Scholar. Clarke, P. G. H., & Whitteridge, D. The projection of the retina, including the 'red area,' on to the optic tectum of the pigeon. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology, 1976, 61, 351-358.
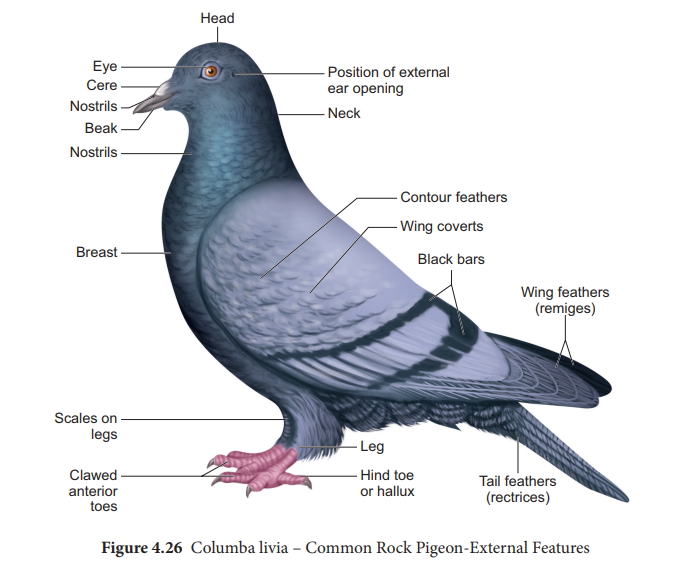
Pigeon (Columba livia) Classification, External features, Exoskeleton, Endoskeleton, Anatomy
Pigeon Anatomy & Physiology: 15 Facts. Although pigeons and doves are a diverse group of birds, they do share some clinically significant anatomy and physiology, including a large, bilobed crop or ingluvies, crop milk production, as well as a vascular plexus found in the subcutis of pigeons. This post also touches on specialized anatomic.

Anatomy Of A Pigeon lupon.gov.ph
Anatomy and Physiology. Atlas of Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. 2: Skeletal systems. 2.5: Pigeon skeleton. Expand/collapse global location.
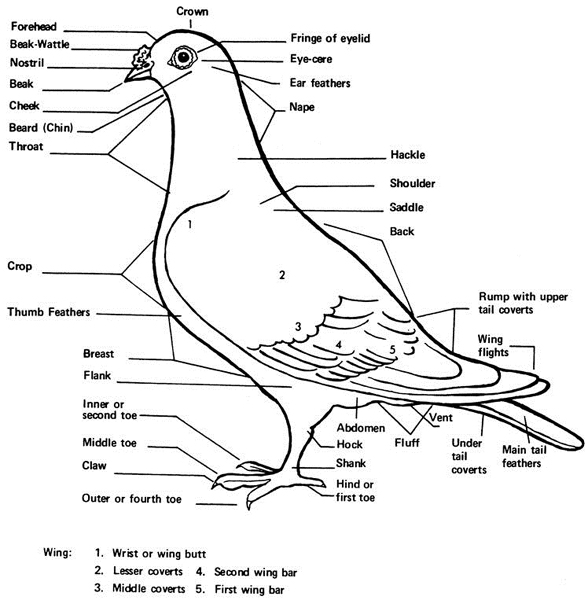
Avian Medical Pages for Pigeons & Doves, plus Hand Feeding.
Anatomy of Pigeon (Columba livia): Endoskeleton, Digestive, Respiratory, Circulatory, Arterial, Nervous, Venous system, receptor organs, Sensor organs. Anatomy Endoskeleton The skeletal system is strong but lightly built. The bones are light and spongy. Many of the long bones contain air instead of marrow (Pneumatic bones).